1. Megatron-LM
commit 94bd476bd840c2fd4c3ebfc7448c2af220f4832b (HEAD -> main, origin/main, origin/HEAD)[1/N]Megatron/megatron/core/pipeline_parallel/p2p_communication.py
_communicate_shapes 和 _communicate 共调用torch.empty()四次。
def _communicate_shapes(tensor_send_next, tensor_send_prev, recv_prev, recv_next, config):
if recv_prev:
recv_prev_shape_tensor = torch.empty(
(3), device=torch.cuda.current_device(), dtype=torch.int64
)
if recv_next:
recv_next_shape_tensor = torch.empty(
(3), device=torch.cuda.current_device(), dtype=torch.int64
)
...创建接收形状的tensor的缓冲区。先init tensor的形状信息,是一个[b,s,h]的三维tensor。
def _communicate(...) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
...
def create_tensor_recv_prev():
return torch.empty(
recv_prev_shape,
requires_grad=True,
device=torch.cuda.current_device(),
dtype=config.pipeline_dtype,
)
def create_tensor_recv_next():
return torch.empty(
recv_next_shape,
requires_grad=True,
device=torch.cuda.current_device(),
dtype=config.pipeline_dtype,
)创建接收数据的tensor的缓冲区。在进行P2P通信之前,让NCCL的irecv操作预先分配好接收缓冲区。
2. Pytorch
2.1 python侧(如何开辟显存)
[2/N]会调用到:megatron → torch/ _refs/ _init_.py 内的empty()
这里主要是对shape和strides做了处理。shape会先检查一下当前是不是元组,比如((1,2,3))就会变成(1,2,3)。然后strides默认会用 make_contiguous_strides_for 这个方法计算步长,得到(6,3,1)。
@out_wrapper()
def empty(
*shape,
dtype: Optional[torch.dtype] = None,
layout: torch.layout = torch.strided,
device: Optional[DeviceLikeType] = None,
requires_grad: bool = False,
pin_memory: bool = False,
memory_format: torch.memory_format = torch.contiguous_format,
) -> TensorLikeType:
...
shape = utils.extract_shape_from_varargs(shape)
if memory_format == torch.contiguous_format:
strides = utils.make_contiguous_strides_for(shape)
elif ...
return torch.empty_strided(
shape,
strides,
dtype=dtype,
layout=layout,
device=device,
pin_memory=pin_memory,
requires_grad=requires_grad,
)[3/N] 从empty()进入到 torch/ _refs/ _init_.py 内的empty_strided()
def empty_strided(shape, strides, *, dtype=None, device=None, layout=torch.strided, requires_grad=False, pin_memory=False):
# 最终调用 prims.empty_strided
return prims.empty_strided(shape, strides, dtype=dtype, device=device, requires_grad=requires_grad)[4/N] prims.empty_strided()会去调用torch/_prims/_init_.py内的_make_prim()
empty_strided = _make_prim(
schema="empty_strided(SymInt[] shape, SymInt[] strides, *, ScalarType dtype, Device device, bool requires_grad) -> Tensor",
return_type=RETURN_TYPE.NEW,
meta=_empty_strided_meta,
impl_aten=torch.empty_strided,
doc=_empty_strided_doc,
)[5/N] _make_prim()内的 _make_prim 再往下就是会调用dispatcher去调aten算子。
2.2 C++侧(如何注册到ncclComm)
CUDA JIT
[6/N] torch/csrc/jit/tensorexpr/cuda_codegen.cpp
由于device是cuda,dispather会选CUDA backend进入 empty_strided_cuda 。
at::Tensor CudaCodeGen::empty_strided(
c10::IntArrayRef size,
c10::IntArrayRef stride,
std::optional<c10::ScalarType> dtype_opt,
std::optional<c10::Layout> layout_opt,
std::optional<c10::Device> device_opt,
std::optional<bool> pin_memory_opt) {
c10::DeviceGuard device_guard(device_opt.value());
return at::native::empty_strided_cuda(
size, stride, dtype_opt, layout_opt, device_opt, pin_memory_opt);
}at::native::empty_strided_cuda的实现:
- 调用
at::detail::empty_strided_cuda函数,实际分配CUDA显存并创建tensor对象 - 文档内的两个torch.use_deterministic_algorithms() 和 torch.utils.deterministic.fill_uninitialized_memory都为true的话就开启。if内的条件1是确定性算法让每次输出一致,条件2是将浮点数和复数值将设为 NaN,整数值将设为最大值。
namespace at::native{
Tensor empty_strided_cuda(...) {
Tensor result = at::detail::empty_strided_cuda(size, stride, dtype_opt, layout_opt, device_opt, pin_memory_opt);
// See Note [Enabling Deterministic Operations]
if (C10_UNLIKELY(at::globalContext().deterministicAlgorithms() && at::globalContext().deterministicFillUninitializedMemory())) {
fill_empty_deterministic_(result);
}
return result;
}
}[8/N] aten/src/ATen/cuda/EmptyTensor.cpp at::detail::empty_strided_cuda
这里主要就是拿到allocator分配器传到通用的empty_strided_generic去,实现如下:
- 初始化cuda上下文
- 设置设备上下文
- get cuda allocator的对象(但是还没实际去申请)
- 设置dispatch的key
- 把allocator和cuda_dks这俩丢进
at::detail::empty_strided_generic
TensorBase empty_strided_cuda(size, stride, dtype, device_opt) {
at::globalContext().lazyInitDevice(c10::DeviceType::CUDA); //init cuda context
const auto device = device_or_default(device_opt);
TORCH_INTERNAL_ASSERT(device.is_cuda());
const DeviceGuard device_guard(device); // 设置设备上下文
auto* allocator = at::cuda::getCUDADeviceAllocator();//获取cuda的分配器
constexpr c10::DispatchKeySet cuda_dks(c10::DispatchKey::CUDA);//设置dispatch的key
return at::detail::empty_strided_generic(
size, stride, allocator, cuda_dks, dtype);
}[9/N] aten/src/ATen/EmptyTensor.cpp at::detail::empty_strided_generic 这里计算了size_bytes字节数,然后和allocator一起传入c10::make_intrusive<StorageImpl>。
static TensorBase _empty_strided_generic(size, stride, allocator, cuda_dks,
ScalarType scalar_type) {
at::detail::check_size_nonnegative(size);
at::detail::raise_warning_for_complex_half(scalar_type);
caffe2::TypeMeta dtype = scalarTypeToTypeMeta(scalar_type);
// 计算所需字节数
auto size_bytes = computeStorageNbytes(size, stride, dtype.itemsize());
// 创建storageImpl
auto storage_impl = c10::make_intrusive<StorageImpl>(
c10::StorageImpl::use_byte_size_t(),
size_bytes,
allocator,
/*resizeable=*/true);
// 创建tensor对象
auto tensor = detail::make_tensor_base<TensorImpl>(
std::move(storage_impl), cuda_dks, dtype);
tensor.unsafeGetTensorImpl()->set_sizes_and_strides(size, stride);
return tensor;
}[10/N] c10/core/StorageImpl.h 假设我们的内存不是开辟在堆上的,前面会触发这里的第二个构造函数的allocator→allocate(size_bytes.as_int_unchecked()),走到cuda内的allocate()方法:
StorageImpl(
use_byte_size_t /*use_byte_size*/,
SymInt size_bytes,
at::DataPtr data_ptr, //后面CUDACachingAllocator::allocate()返回的GPU内存指针
at::Allocator* allocator,
bool resizable)
: data_ptr_(std::move(data_ptr)),
size_bytes_(std::move(size_bytes)),
size_bytes_is_heap_allocated_(size_bytes_.is_heap_allocated()),
resizable_(resizable),
received_cuda_(false),
allocator_(allocator) {
if (resizable) {
TORCH_INTERNAL_ASSERT(
allocator_, "For resizable storage, allocator must be provided");
}
refresh_has_data_ptr_check();
}
StorageImpl(
use_byte_size_t /*use_byte_size*/,
const SymInt& size_bytes,
at::Allocator* allocator,
bool resizable)
: StorageImpl( //又委托给了第一个构造函数
use_byte_size_t(),
size_bytes,
size_bytes.is_heap_allocated() //关键 等会看一下怎么走的
? allocator->allocate(0)
: allocator->allocate(size_bytes.as_int_unchecked()),
allocator,
resizable) {}后续则需要在这里拿到gpu内存,也就是StorageImpl内的
DataPtr data_ptr_;这个丢给ncclCommRegister。
[11/N] c10/cuda/CUDACachingAllocator.cpp:3805 这里会去调用具体设备的分配器 (关键!)
// 在 NativeCachingAllocator 类中
DataPtr allocate(size_t size) override {
constexpr size_t one_exa_bytes = 1152921504606846976ULL;
TORCH_CHECK_WITH(
OutOfMemoryError,
size < one_exa_bytes,
"CUDA out of memory. Tried to allocate more than 1EB memory.");
c10::DeviceIndex device = 0;
C10_CUDA_CHECK(c10::cuda::GetDevice(&device));
void* devPtr = nullptr;
void (*deleteFunc)(void*) = &local_raw_delete;
CUDAStream stream = cuda::getCurrentCUDAStream(device);
if (forceUncachedAllocator() || !isEnabled()) {
deleteFunc = &uncached_delete;
devPtr = uncached_allocate(size); // 调试模式:调cudaMalloc
} else {
if (size != 0) {
// 走到1318行的Block* malloc()
this->malloc(&devPtr, device, size, stream);// 正常模式:通过缓存分配器分配
}
}
if (size && TORCH_SDT_IS_ENABLED(malloc)) {
TORCH_SDT_WITH_SEMAPHORE(malloc, devPtr, device, size, stream.id());
}
return {devPtr, devPtr, deleteFunc, Device(DeviceType::CUDA, device)};
}这里的this→allocate会走到DeviceCachingAllocator类内的void malloc()方法:
void malloc(void** devPtr, c10::DeviceIndex device, size_t size, cudaStream_t stream) {
// 1. 验证设备索引有效性
TORCH_INTERNAL_ASSERT(0 <= device && device < device_allocator.size(), ...);
// 2. 调用具体设备的分配器 (关键!)
Block* block = device_allocator[device]->malloc(device, size, stream);
// 3. 将block添加到全局追踪表
add_allocated_block(block);
// 4. 返回GPU内存指针
*devPtr = (void*)block->ptr;
// 5. 追踪内存分配 (用于调试)
// ...
}device→malloc的实现是:
Block* malloc(c10::DeviceIndex device,size_t orig_size,cudaStream_t stream) {
// 0. 获取cudaGraph内存池或默认内存池
auto& pool = get_pool(size, stream); // pool和ncclMempool????
const size_t alloc_size = get_allocation_size(size);
AllocParams params(device, size, stream, &pool, alloc_size, stats);
// 1. 处理缓存逻辑
bool block_found = get_free_block(params) || ...;
// 2. 如果缓存中没找到,分配新内存
if (!block_found) {
block_found = alloc_block(params, false, context, lock) || ...;
}
// 3. 最终调用 cudaMalloc 分配GPU内存
/*
// 在 alloc_block 中
p.err = cudaMallocMaybeCapturing(&ptr, size, p);
// 在 cudaMallocMaybeCapturing 中
return allocPrimitive(ptr, size, p);
// 在 allocPrimitive 中
return C10_CUDA_ERROR_HANDLED(cudaMalloc(ptr, size)); // 最终调用!
*/
// 4. 返回包装好的Block对象
return alloc_found_block(params, orig_size, context, split_remainder);
}[12/N] CUDACachingAllocator内每个device的分配器用 cudaMalloc/cudaMallocAsync 开辟出的 segment,这个segment内会生成:
// alloc_found_block内会 record_trace
TraceEntry { action_ = SEGMENT_ALLOC, // SEGMENT_ALLOC, SEGMENT_FREE等
addr_ = segment_base_ptr,// GPU内存地址
size_ = segment_size, // 内存大小
stream_ = stream, // CUDA stream
device_ = device_id, // GPU设备id
mempool_= mempool_id, // 内存池子id
cuda上下文}然后所有的TraceTracker(attachAllocatorTraceTracker)会收到这个TraceEntry。而tracker是在NCCL backend在初始化的统一挂上的。
summary
每个deviceallocator为什么要有tracker?NCCL需要知道哪个GPU内存可以用于communication,每个allocator内的tracker负责通知nccl什么时候有新的malloc 什么时候有新的free。 而刚刚的TraceEntry就包含了NCCL需要的所有信息 。
NCCL怎么拿到这些信息去register?构造ProcessGroupNCCL的时候就注册hook,当cudaMalloc一完成,就会通过 cacheAllocatorRegisterHook 这个钩子直接知道是SEGMENT_ALLOC的动作,所以立刻去TraceEntry拿出addr_和size_去完成注册。
NCCL Backend
[13/N] torch/csrc/distributed/c10d/ProcessGroupNCCL.cpp
如果是ProcessGroupNCCL 的构造函数内并且开启了 shouldAllCommunicatorsRegisterAllTensors 就会调用 attachAllocatorHooks 去挂hook。
[14/N] 342:torch/csrc/distributed/c10d/ProcessGroupNCCL.cpp
attachAllocatorHooks 使用 attachAllocatorTraceTracker 管理 cacheAllocatorRegisterHook 和 cacheAllocatorDeregisterHook 去把hook绑定到分配器上,也就是SEGMENT_ALLOC和SEGMENT_FREE。
[15/N] 302:320:torch/csrc/distributed/c10d/ProcessGroupNCCL.cpp
cacheAllocatorRegisterHook内是通过调用 registerSegment 收到SEGMENT_ALLOC后,hook就回去遍历同一个GPU上所有的NCCL Communicator。注册HOOK遵循两个条件:
- if 设置了 “全部 comm 全部段统一登记” 环境变量,就给所有 comm 注册;
- else 就只注册与当前mem-pool关联的comm。
[16/N] 366:400:torch/csrc/distributed/c10d/NCCLUtils.cpp
NCCLComm::registerSegment调用的是真正的NCCL API。这里的核心逻辑就是三部:
1)上mutex锁和检查ptr是不是已经注册过。注册过会打印 Segment with ptr has already been registered on ncclComm。
2)调用底层NCCL API
- 普通内存:
ncclCommRegister(comm, ptr, size, &handle) - 对称内存(window):
ncclCommWindowRegister(comm, ptr, size, (ncclWindow_t*)&handle, NCCL_WIN_COLL_SYMMETRIC)3)返回的handle存到registeredSegmentHandles_[ptr]在后续deregisterSegment()使用。 该显存段就“告诉”了 NCCL runtime,后续同一进程里的所有 CC/ P2P 操作都可以 零拷贝 地直接访问这块显存。
[17/N] 432:torch/csrc/distributed/c10d/NCCLUtils.cpp 当分配器真正回收 segment 时会产生 SEGMENT_FREE TraceEntry,cacheAllocatorDeregisterHook → ncclComm→deregisterSegment(ptr),调用 ncclCommDeregister 或 ncclCommWindowDeregister 把 handle 清掉。
3. NCCL
https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/nccl/user-guide/docs/usage/bufferreg.html#mem-allocator
注册cuda分配的内存
ProcessGroupNCCL.cpp内有三处会对CUDA的内存送给NCCL Comm:
initNCCLComm内会在新NCCL Comm创建后立即注册现有的内存段,确保可以访问已分配的CUDA内存。并将ncclComm放到了MemPoolMap内,给后面cacheAllocatorRegisterHook用。cacheAllocatorRegisterHook会自动将CUDA新分配的内存段注册到相应的NCCL comm内。registerMemPool将特定的MemPool注册到NCCL的comm内。
static void cacheAllocatorRegisterHook(
const c10::cuda::CUDACachingAllocator::TraceEntry& te) {
// Register after SEGMENT_ALLOC
if (te.action_ !=
c10::cuda::CUDACachingAllocator::TraceEntry::Action::SEGMENT_ALLOC) {
return;
}
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(ncclCommMemPoolMapMutex);
for (auto& [ncclComm, memPools] : ncclCommMemPoolMap) {
if (te.device_ == ncclComm->getDeviceIndex()) {
if (shouldAllCommunicatorsRegisterAllTensors() ||
memPools.find(te.mempool_) != memPools.end()) {
// NOLINTNEXTLINE(performance-no-int-to-ptr)
ncclComm->registerSegment(reinterpret_cast<void*>(te.addr_), te.size_);
}
}
}
}4. Env setup
git clone好pytorch之后,先下载所有三方包:
git submodule update --init --recursive编译pytorch:
#!/bin/bash
set -e
export NCCL_ROOT=/workspace/infrawaves/share/liuda/vc226/vccl_2.26.6-1/build
export NCCL_INCLUDE_DIR=${NCCL_ROOT}/include
export NCCL_LIB_DIR=${NCCL_ROOT}/lib
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=${NCCL_LIB_DIR}:${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}
export CMAKE_GENERATOR=Ninja
export MAX_JOBS=64
export USE_CUDA=1
export USE_NCCL=1
export USE_SYSTEM_NCCL=1
export PYTORCH_SKIP_NCCL_SUBMODULE=1
python setup.py develop清理pytorch:
// 局部
cd build
rm -r 某个
// 全局
python setup.py clean5. Use nccl alloc and free
方案一:
g++ -shared -o minide.so minide.cpp -ldl -fPIC -I/usr/local/cuda/include -I./spdlog/include使用上面shell编译如下代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <cuda.h>
#include <nccl.h>
#include <cublas_v2.h>
#include <dlfcn.h>
#include <vector>
#include <thread>
#include <memory>
#include <atomic>
#include "spdlog/include/spdlog/spdlog.h"
#include "spdlog/include/spdlog/async.h"
#include "spdlog/include/spdlog/sinks/basic_file_sink.h"
#include <iomanip>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
typedef cudaError_t (*cudaMalloc_t)(void**, size_t);
typedef cudaError_t (*cudaFree_t)(void*);
typedef CUresult (*cuMemCreate_t)(CUmemGenericAllocationHandle*, size_t, const CUmemAllocationProp*, unsigned long long);
typedef ncclResult_t (*ncclMemAlloc_t)(void**, size_t);
typedef ncclResult_t (*ncclMemFree_t)(void*);
static cudaMalloc_t real_cudaMalloc = nullptr;
static cudaFree_t real_cudaFree = nullptr;
static cuMemCreate_t real_cuMemCreate = nullptr;
static ncclMemAlloc_t real_ncclMemAlloc = nullptr;
static ncclMemFree_t real_ncclMemFree = nullptr;
static bool use_nccl_allocator = true;
void init_nccl_mem_functions() {
static bool initialized = false;
if (initialized) return;
void* nccl_handle = dlopen("/workspace/infrawaves/share/liuda/vc226/vccl_2.26.6-1/build/lib/libnccl.so", RTLD_LAZY | RTLD_GLOBAL);
if (!nccl_handle) {
printf("warning: cant open my vccl");
return;
}
real_ncclMemAlloc = (ncclMemAlloc_t)dlsym(nccl_handle, "ncclMemAlloc");
real_ncclMemFree = (ncclMemFree_t)dlsym(nccl_handle, "ncclMemFree");
if (!real_ncclMemAlloc || !real_ncclMemFree) {
printf("Warning: Cannot find ncclMemAlloc/ncclMemFree symbols: %s\n", dlerror());
use_nccl_allocator = false;
dlclose(nccl_handle);
return;
}
initialized = true;
}
extern "C" cudaError_t cudaMalloc(void** devPtr, size_t size) {
if (!real_cudaMalloc) {
real_cudaMalloc = (cudaMalloc_t)dlsym(RTLD_NEXT, "cudaMalloc");
}
if (use_nccl_allocator) {
init_nccl_mem_functions();
if (real_ncclMemAlloc) {
ncclResult_t nccl_result = real_ncclMemAlloc(devPtr, size);
if (nccl_result == ncclSuccess) {
return cudaSuccess;
} else {
printf("rank %s ncclMemAlloc FAILED: %d, falling back to cudaMalloc\n",
getenv("OMPI_COMM_WORLD_RANK"), nccl_result);
}
}
}
return real_cudaMalloc(devPtr, size);
}
extern "C" cudaError_t cudaFree(void* devPtr) {
if (!real_cudaFree) {
real_cudaFree = (cudaFree_t)dlsym(RTLD_NEXT, "cudaFree");
}
if (use_nccl_allocator && real_ncclMemFree) {
ncclResult_t nccl_result = real_ncclMemFree(devPtr);
if (nccl_result == ncclSuccess) {
return cudaSuccess;
} else {
printf("rank %s ncclMemFree FAILED: %d, falling back to cudaFree\n",
getenv("OMPI_COMM_WORLD_RANK"), nccl_result);
}
}
return real_cudaFree(devPtr);
}
extern "C" CUresult cuMemCreate(CUmemGenericAllocationHandle* handle, size_t size,
const CUmemAllocationProp* prop, unsigned long long flags) {
if (!real_cuMemCreate) {
real_cuMemCreate = (cuMemCreate_t)dlsym(RTLD_NEXT, "cuMemCreate");
}
printf("rank %s cuMemCreate intercepted: size = %zu, flags = %llu\n",
getenv("OMPI_COMM_WORLD_RANK"), size, flags);
// use ori cuMemCreate
CUresult result = real_cuMemCreate(handle, size, prop, flags);
if (result == CUDA_SUCCESS) {
printf("rank %s cuMemCreate SUCCESS: handle = %p\n",
getenv("OMPI_COMM_WORLD_RANK"), (void*)*handle);
} else {
printf("rank %s cuMemCreate FAILED: result = %d\n",
getenv("OMPI_COMM_WORLD_RANK"), result);
}
return result;
}
extern "C" void set_nccl_allocator_enabled(bool enabled) {
use_nccl_allocator = enabled;
printf("rank %s NCCL allocator %s\n",
getenv("OMPI_COMM_WORLD_RANK"), enabled ? "ENABLED" : "DISABLED");
}
extern "C" bool is_nccl_allocator_enabled() {
return use_nccl_allocator && real_ncclMemAlloc && real_ncclMemFree;
}
将生成的so挂载到使用的mpirun的shell内:
mpirun ...\
-x LD_PRELOAD=/path/minide.so \
...
python train.py跑训练可以看到所有的cudaMalloc和cudaFree都变成了nccl内的ncclMemAlloc和ncclMemFree:
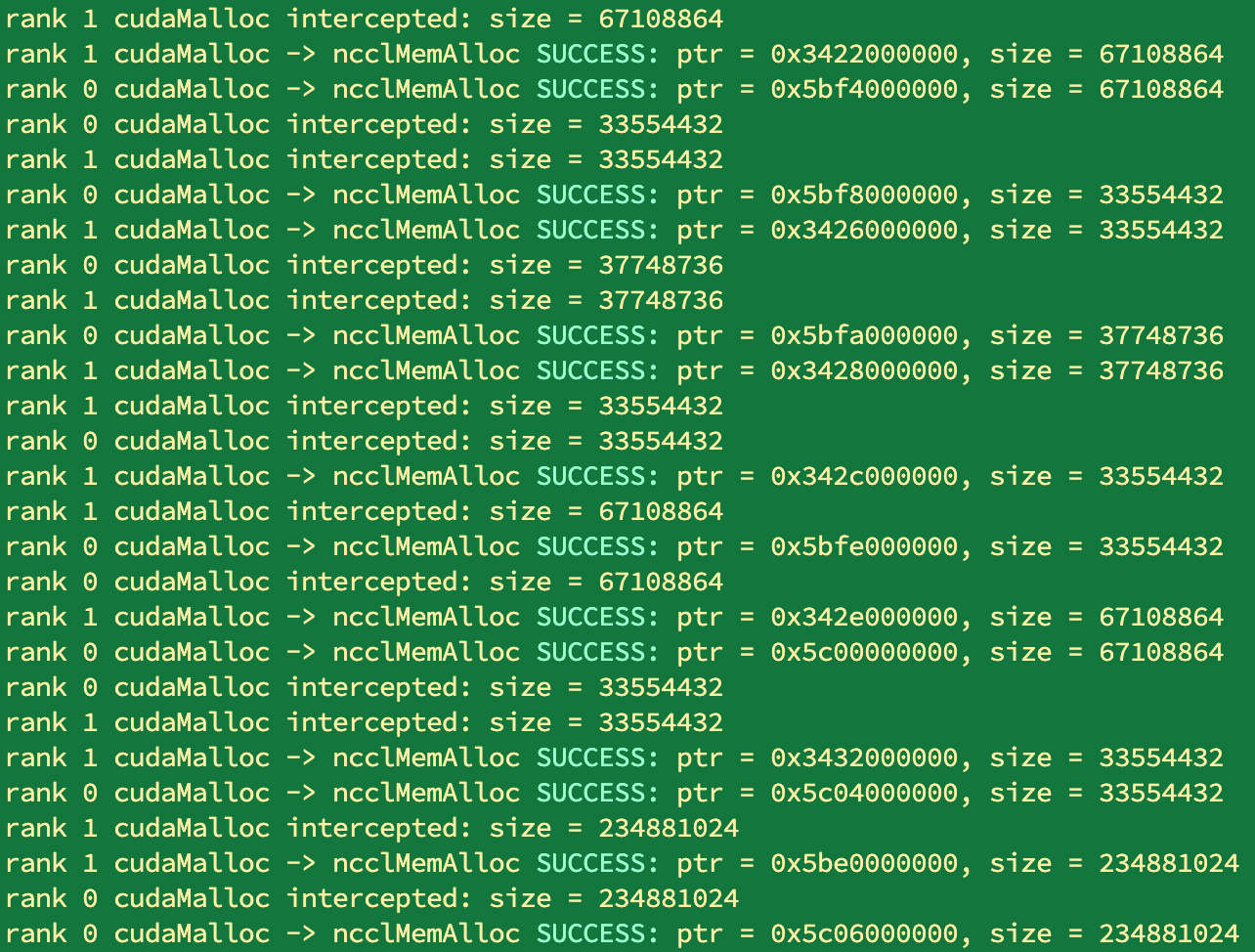
 register的话目前先用:
register的话目前先用:
NCCL_API(ncclResult_t, ncclSend, const void* sendbuff, size_t count, ncclDataType_t datatype, int peer,
ncclComm_t comm, cudaStream_t stream);
ncclResult_t ncclSend(const void* sendbuff, size_t count, ncclDataType_t datatype, int peer,
ncclComm_t comm, cudaStream_t stream) {
NVTX3_FUNC_WITH_PARAMS(Send, NcclNvtxParamsSendRecv,
NVTX3_PAYLOAD(comm ? comm->commHash : 0, count * ncclTypeSize(datatype), peer));
void *handle = NULL;
ncclResult_t result = ncclCommRegister(comm, (void *)sendbuff, count * ncclTypeSize(datatype), NULL);
if (result != ncclSuccess) {
return result;
}
struct ncclInfo info = { ncclFuncSend, "Send",
NULL, (void*)sendbuff, count, datatype, ncclSum, peer, comm, stream, /* Args */
1, 1 };
return ncclEnqueueCheck(&info);
}
NCCL_API(ncclResult_t, ncclRecv, void* recvbuff, size_t count, ncclDataType_t datatype, int peer,
ncclComm_t comm, cudaStream_t stream);
ncclResult_t ncclRecv(void* recvbuff, size_t count, ncclDataType_t datatype, int peer,
ncclComm_t comm, cudaStream_t stream) {
NVTX3_FUNC_WITH_PARAMS(Recv, NcclNvtxParamsSendRecv,
NVTX3_PAYLOAD(comm ? comm->commHash : 0, count * ncclTypeSize(datatype), peer));
void *handle = NULL;
ncclResult_t result = ncclCommRegister(comm, recvbuff, count * ncclTypeSize(datatype), &handle);
if (result != ncclSuccess) {
return result;
}
struct ncclInfo info = { ncclFuncRecv, "Recv",
NULL, recvbuff, count, datatype, ncclSum, peer, comm, stream, /* Args */
1, 1 };
return ncclEnqueueCheck(&info);
}